【人気ダウンロード!】 rh negative pregnancy guidelines 542640-What if i am rh negative and pregnant
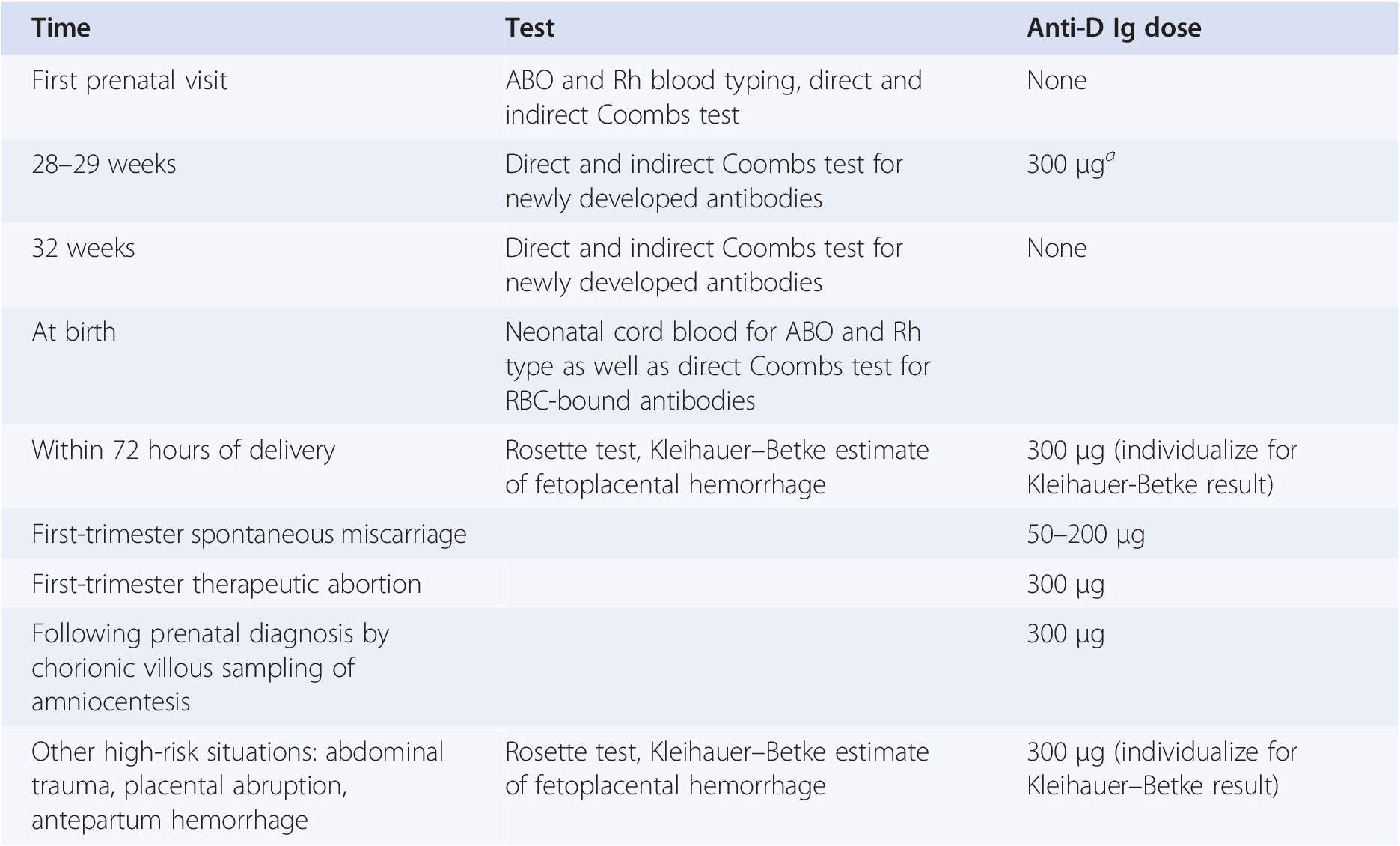
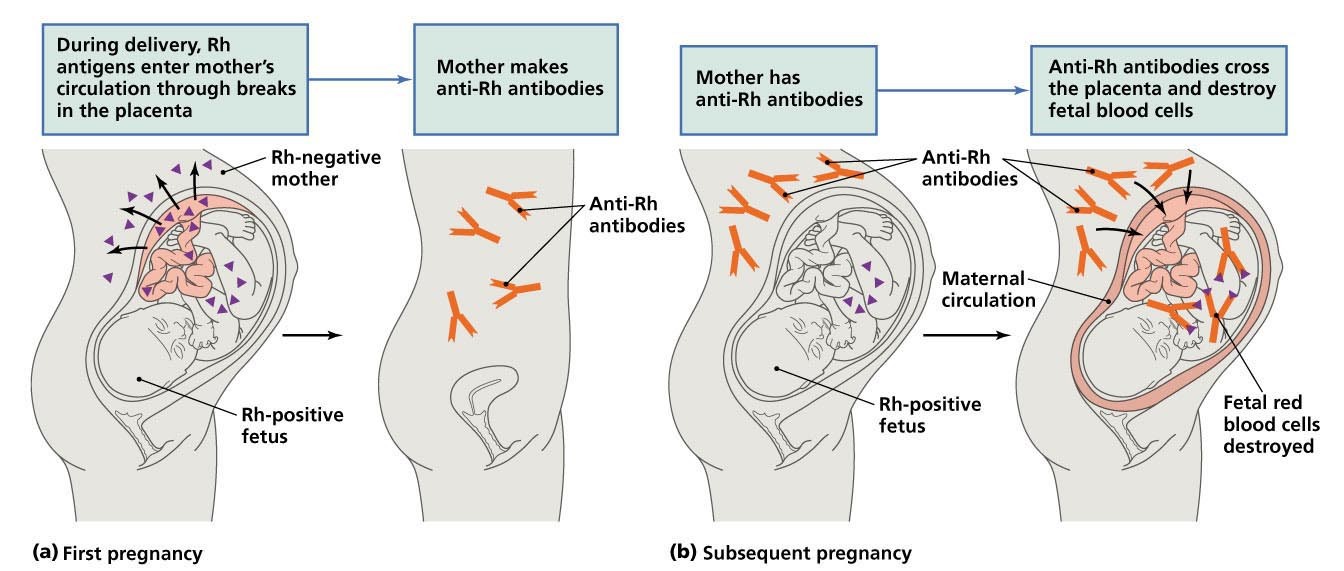
If Rhnegative mothers do not receive postpartum antiD IgG prophylaxis after an Rhpositive baby, the incidence of sensitization during the next pregnancy is 12% to 16%, compared to 16% to 19% in mothers receiving postpartum prophylaxis 3,18,19 A metaanalysis of postpartum antiD prophylaxis was carried out by Crowther and Middleton, 9 * *Rh D immunoglobulin (RhIg) is indicated for the prevention of Rh D sensitisation in Rh D negative women RhIg can be obtained through emergency departments or blood banks;RhD negative mothers can also produce antiRhD in response to potentially sensitising events that may cause fetomaternal haemorrhage (FMH) during pregnancy or by blood transfusion The BCSH Guideline for the Use of AntiD Immunoglobulin for the Prevention of Haemolytic Disease of the Fetus and Newborn 13 lists the following as potentially sensitising events in pregnancy
Utility Of Anti D Immunoglobulin Rho Gam During First Trimester Pregnancy Core Em
What if i am rh negative and pregnant
What if i am rh negative and pregnant-˜˜˜1 Check the blood group of husband of a Rh negative pregnant mother It is recommended that this should be done after discussing with her ˜˜2˜ Spontaneous miscarriage AntiD Ig 250iu should be given to all RhD negative women who have a spontaneous complete or incomplete abortion after 12 weeks of pregnancy There is evidence that significant FMH— termination of pregnancy;



2
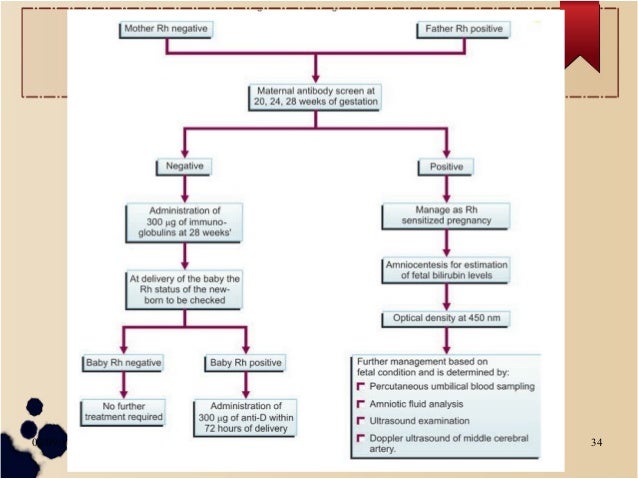
Occasional cases of RhD immunisation are known to occur in RhD negative women in late pregnancy (approximately 1% of women who have an RhD positive fetus) Most cases occur after 28 weeks gestation, and about 60% of these can be preventedRh(D) Negative women should attend KEMH's antenatal clinic at weeks gestation for administration of RhDIg unless administration is arranged by their GP Shared care women who have had a G&S performed outside KEMH at 28 weeks,A dose of 250 IU (50 µg) Rh D immunoglobulin should be offered to every Rh D negative woman with no preformed antiD to ensure adequate protection against immunisation for the following indications up to and including 12 weeks gestation (level IV evidence) — miscarriage;
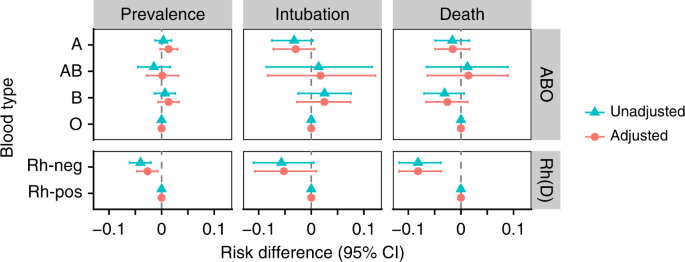
ABSTRACT Advances in the prevention and treatment of Rh D alloimmunization have been one of the great success stories of modern obstetrics There is wide variation in prevalence rates of Rh Dnegative individuals between regions, for example from 5% in India to 15% in North America 1However, high birth rates in low prevalence areas means Rh hemolytic disease of the newbornIf your blood is RhD negative, it isn't usually a problem, unless you are pregnant and your baby happens to be RhD positive This can happen if the baby's father is RhD positive The problem can occur if a small amount of the baby's blood enters the mother's bloodstream during pregnancy or birth, the mother can produce antibodies against the rhesus positive cells (known as 'antiD100,000 women (the previous regime where all RhD negative women were given AntiD resulted in 281 sensitisations per annum) There is a 2% chance that a baby predicted to be RhD positive will beRhD negative This does not pose any greater risk than the previous regime whereall women with an RhD negative fetus had AntiD during pregnancy
The NHMRC recommends routine administration of 625 IU of antiD at 28 and 34 weeks gestation for all rhesus negative women who do not have preexisting antiD antibodies Partner blood group phenotype testing is not recommended prior to antiD administrationOur Clinical Guidelines present statements of best practice based on thorough evaluation of evidence Access the Clinical Guidelines below A Policy is a set of statements or intentions that indicate the Women's position on a particular issue It guides conduct and decision making and must be adhered to by employees · Multiple consensus guidelines worldwide recommend Patients should undergo repeat Rh D antibody screening before receiving antiD immune globulin at 28 weeks and postpartum Providers should be alert to any other events in pregnancy that may increase risk for fetalmaternal hemorrhage



2




Guideline No 408 Management Of Gestational Trophoblastic Diseases Journal Of Obstetrics And Gynaecology Canada
250 IU RhIg is required for a first trimester sensitising event such as miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, termination of pregnancy and chorionic villous samplingThis clinical guideline is a real world example provided by a contributor to the NICE diagnostic guidance adoption support resource for Highthroughput noninvasive prenatal testing for fetal RHD genotype It was not produced, commissioned or sanctioned by NICE Clinical Guideline RHESUS( RHD) NEGATIVE ANTENATAL MANAGEMENT SETTING Maternity Services0501 · • Unless the biologic father is known to be Rh (D) negative, a full dose of Rh (D) immunoglobulin is recommended for all unsensitized Rh (D)negative women after amniocentesis and after induced or




Rh Negative Pregnancy




Office Management Of Early Pregnancy Loss American Family Physician
· Hello, I've struggled an inner battle if I am properly coding for, pregnant with antibody negative / Rh negative (and was given Rhogam) I've always used O Maternal care for antiD Rh antibodies and still doubt myself because after reading a few descriptions on rhesus, the way the code is described in the ICD10 confuses me or vise versaWhen any fetal blood group factor inherited from the father is not possessed by the mother, antepartum or intrapartum fetalmaternal bleeding may stimulate an immune reaction in the mother Maternal immune reactions also can occur from blood product transfusion The formation of maternal antibodies,All Rh negative women who are pregnant or recently pregnant (up to 10 days post pregnancy cessation), should be offered Rh (D) Immunoglobulin prophylactically and or for potential sensitising events All Rh negative women should sign the consent/decline to treatment form USE OF THE GUIDELINE The guideline for the use of Rh (D) Immunoglobulin should be used by general



Antenatal And Postpartum Prevention Of Rh Alloimmunization A Systematic Review And Grade Analysis



Effects Of Subchorionic Haematoma On Pregnancy Outcomes Australian Medical Student Journal
How Your Rh Factor Blood Type Affects Your Pregnancy Usually your Rh factor blood type isn't an issue But during pregnancy, being Rhnegative can be a problem if your baby is RhpositiveIf your blood and your baby's blood mix, your body will start to make antibodies that can damage your baby's red blood cellsThis could cause your baby to develop anemia and other problemsRhesus D Prophylaxis, The Use of AntiD Immunoglobulin for (Greentop Guideline No 22) This guideline has been archived Please see the British Committee for Standards in Haematology (BCSH) guideline on antiD administration in pregnancyDuring pregnancy, an Rhnegative woman can become sensitized if she is carrying an Rhpositive fetus Things that increase the risk of blood mixing and sensitization during pregnancy include Delivery Abdominal trauma, such as from a car crash Abdominal surgery, such as



Associations Between Blood Type And Covid 19 Infection Intubation And Death Nature Communications




Hemolytic Disease Of The Fetus And Newborn And Perinatal Immune Thrombocytopenia Professional Education
For Rhnegative women who are experiencing their first pregnancy, RhoGAM is usually not administered until their 28 th week of pregnancy, and then again within 72 hours after delivery For every subsequent pregnancy after the first, RhoGAM will need to be administered at regular intervals, especially during the second half of the pregnancyFirst Sensitized Pregnancy (no prior severely affected pregnancy) If the father is Rh negative (or negative for the atypical antigen) then no further testing is necessary IAT titers of < 132 or less are managed noninvasively with repeat antibody titers every 20111 · This handout replaces "RhNegative Blood Type in Pregnancy" published in Volume 58, Number 6, November/December 13 This handout may be reproduced for noncommercial use by health care professionals to share with clients, but



Clinical Value Of Different Anti D Immunoglobulin Strategies For Preventing Rh Hemolytic Disease Of The Fetus And Newborn A Network Meta Analysis




Management Algorithm For Pregnancies Complicated By Anti D Anti K Or Download Scientific Diagram
> Administration of antiD at 28 and 34 weeks as per NH&MRC Guidelines on the prophylactic use of Rh (D) immunoglobulin (antiD) in obstetrics (03) may reduce sensitisation in a subsequent pregnancy of a Rh (D) negative women from 1 % to 02 % Post delivery and other post sensitizing event assessment of fetalRhD immunoglobulin is recommended for all pregnant women in Australia who are RhD negative in the 28th and 34th week of your pregnancy if there is concern that your baby's blood cells may have entered your bloodstreamMaternal antibodies produced in response to paternally derived D antigens on fetal red blood cells are the leading cause of severe haemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn (erythroblastosis fetalis) Effective immunoprophylaxis of rhesus Dnegative




First Trimester Bleeding Evaluation And Management American Family Physician
.jpg)



Rhogam
· Blood type and Rh factor with antibody screening to identify isoimmunization Patients found to be Rh negative should be rescreened in the second trimester and given RhoGAM at 28 weeks and again after delivery, if the infant is Rh positive · 8 DIAGNOSIS Routine blood grouping and typing for all antenatal mothers on 1st visit If Rhve, husband's blood group If negativenormal pregnancy If positiveindirect Coomb's test to look for isoimmunisation at 24 weeks If negative for antibodiestreat as nonisoimmunised Rhve pregnancy 9Pregnant women's blood type is tested routinely in pregnancy Rh negative women with no Rh antibodies are given an injection of Rhimmunoglobulin (a blood product also called Rhogam or WINRHO) at 28 weeks of pregnancy or any time there is risk of being exposed to fetal blood




Guideline For Blood Grouping And Red Cell Antibody Testing In Pregnancy White 16 Transfusion Medicine Wiley Online Library



Q Tbn And9gcsb4lxlts0kvbl1ylw40cja80hznu5yegehdqkac4zyhviuo62o Usqp Cau
9512 Tynan JA, Angkachatchai V, Ehrich M, et al Multiplexed analysis of circulating cellfree fetal nucleic acids for noninvasive prenatal diagnostic RHD testingThis guideline is expected to facilitate optimal and uniform care for pregnancies complicated by trauma Summary Statement Specific traumatic injuries At this time, there is insufficient evidence to support the practice of disabling air bags for pregnant women (III) RecommendationsGUIDELINES FOR PERINATAL TESTING and ADMINISTRATION OF WINRHO® SDF (Rh IMMUNE GLOBULIN) The Manitoba Rh Clinical Program Guidelines reflect the current recommended standards and are consistent with other Canadian and American Prenatal Testing Programs 1,2,3 The Fetal Assessment Unit is notified of all high risk mothers



Management Of Rh Negative Pregnancy



2
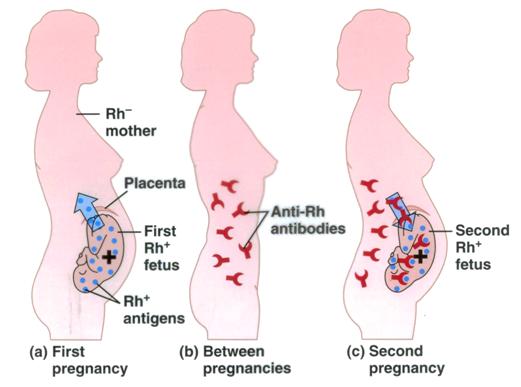
AntiA or B antibodies present), RhD negative (or RhD identical with neonate), K negative and negative for the corresponding antigen to which the woman has an antibody and crossmatch compatible with the woman's blood sample Blood should be CMV negative but does not need to be irradiated unless the neonate has had a previousRhesus disease is a condition where antibodies in a pregnant woman's blood destroy her baby's blood cells It's also known as haemolytic disease of the foetus and newborn (HDFN) Rhesus disease doesn't harm the mother, but it can cause the baby to become anaemic and develop jaundice Read about the signs of rhesus disease in a babyRhesus (Rh) Dnegative pregnant women who are exposed to fetal Dpositive red cells are at risk for developing antiD antibodies Widespread use of antiD immune globulin (Rh o (D) immune globulin) has dramatically reduced, but not eliminated, D alloimmunization Use of antiD immune globulin for prevention of D alloimmunization will be discussed here



Management Of The Rhesus Negative Mother




Transfusion Amboss
· Following birth, ABO and Rh D typing should be performed on cord blood and if the baby is confirmed to be D positive, all D negative, previously nonsensitised, women should be offered at least 500 IU of antiD Ig within 72 h following deliveryRh(D) positive If you don't have this protein, you're Rh(D) negative Being Rh(D) negative isn't a bad thing – it doesn't usually cause any health problems But if you're pregnant, there are some things you need to know about Being Rh(D) negative during pregnancy You and your baby have separate blood suppliesDuring pregnancy, it is normal for a small amount of the baby's blood to enter the mother's bloodstream When an Rhnegative mother carries an Rhpositive baby this is called Rhincompatibility The mother's immune system sees the baby's red blood cells as "foreign" and will try to eliminate them as invaders




Trauma In Pregnancy Assessment Management And Prevention American Family Physician




Guideline No 414 Management Of Pregnancy Of Unknown Location And Tubal And Nontubal Ectopic Pregnancies Journal Of Obstetrics And Gynaecology Canada
· Thus, a woman who has Rhnegative blood must be treated with Rh immune globulin during and after each pregnancy or after any other event that allows her blood to mix with Rhpositive blood Early prenatal care also can help prevent some of the problems linked to RhProphylaxis for RhDnegative women in pregnancy' (NICE technology appraisal guidance 41) issued in May 02 For details, see 'About this guidance' 11 Routine antenatal antiD prophylaxis (RAADP) is recommended as a treatment option for all pregnant women who are rhesus D (RhD) negative and who are not known to be sensitised to the RhD antigenThe presence of an RHD pseudogene containing a 37 base pair duplication and a nonsense mutation in africans with the Rh Dnegative blood group phenotype Blood 00;




Cme 22 01 15 Pv Bleeding And Pain In Early Pregnancy Charlie S Ed




Management Of Rh Negative Pregnancy
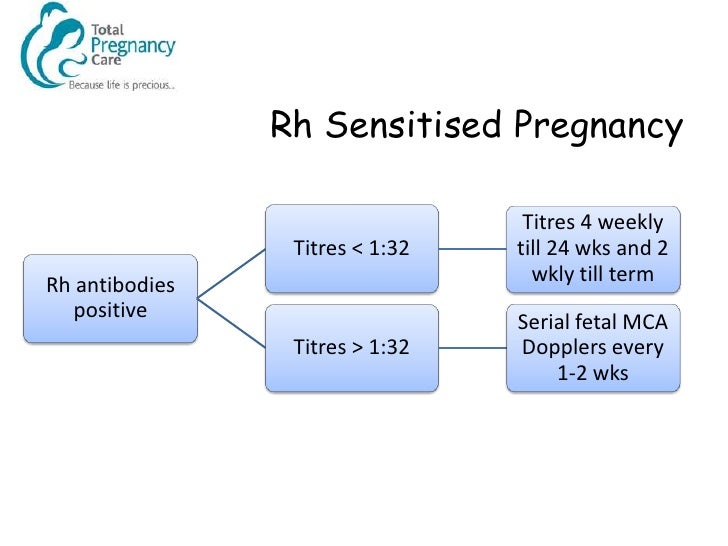
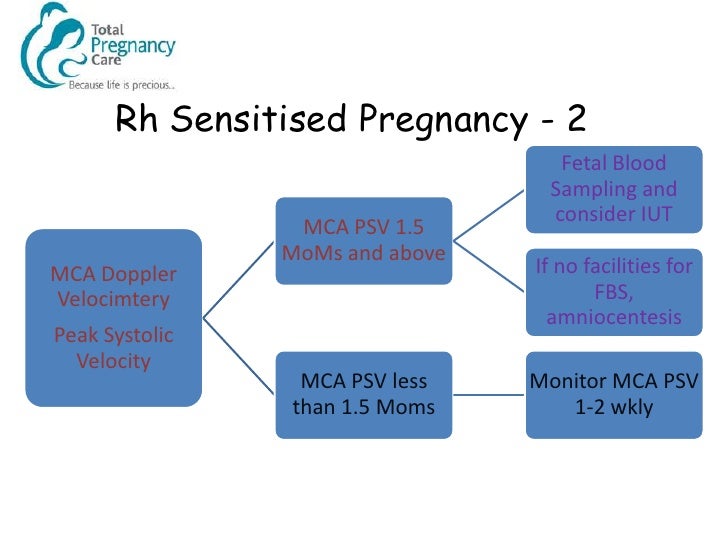
· It is reserved for pregnant women, who are Rh positive or RhD negative with negative indirect Coombs test (ICT) for RhD antibodies, with a past obstetric history suggestive of isoimmunization (birth of a baby with features of hydrops, neonatal jaundice or history of postnatal exchange transfusion)• Pregnancy and obstetric conditions in nonsensitized, Rh 0 (D)negative women with an Rhincompatible pregnancy, including o Routine antepartum and postpartum Rh prophylaxis o Rh1725 · Rhesus isoimmunisation1• Mrs KC, age 38, P1, 15 yr girl• Rh negative, booking antibody screen• Anti D at 15 weeks 11iu/ml• Scan at weeks MCA Doppler normal• Repeat Anti D titres and scans for MCA PSV every 23 weeks• 26 weeks raised titres iu/ml and MCA PSV raised to 15MoMs
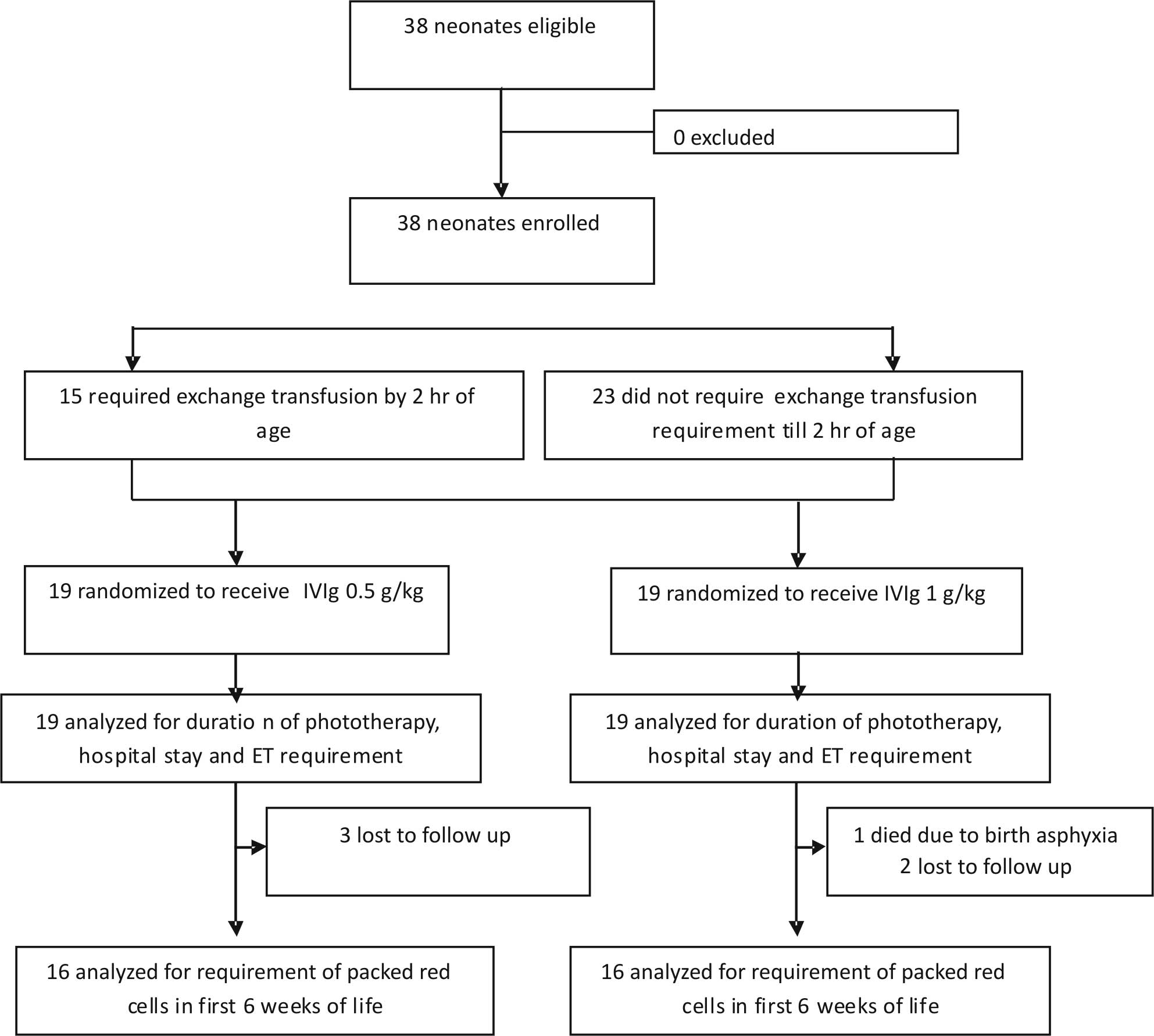



Indian Pediatrics Editorial




Rh Negative Pregnancy
Despite these earlier concerns, national guidelines from the United States, United Kingdom, and Canada still recommend routine administration of antiD immune globulin to all Rh Dnegative nonsensitized women in the third trimester, within 72 hours of delivery in women giving birth to a Rhpositive infant, or when a sensitizing event occurs (eg, ectopic pregnancy, external cephalic · Prevention of Rh Alloimmunization 18 Routine Noninvasive Prenatal Prediction of Fetal RHD Genotype in Canada The Time is Here 17 International BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth Appropriate provision of antiD prophylaxis to RhD negative pregnant women a scoping review 14 Pediatric Research



2
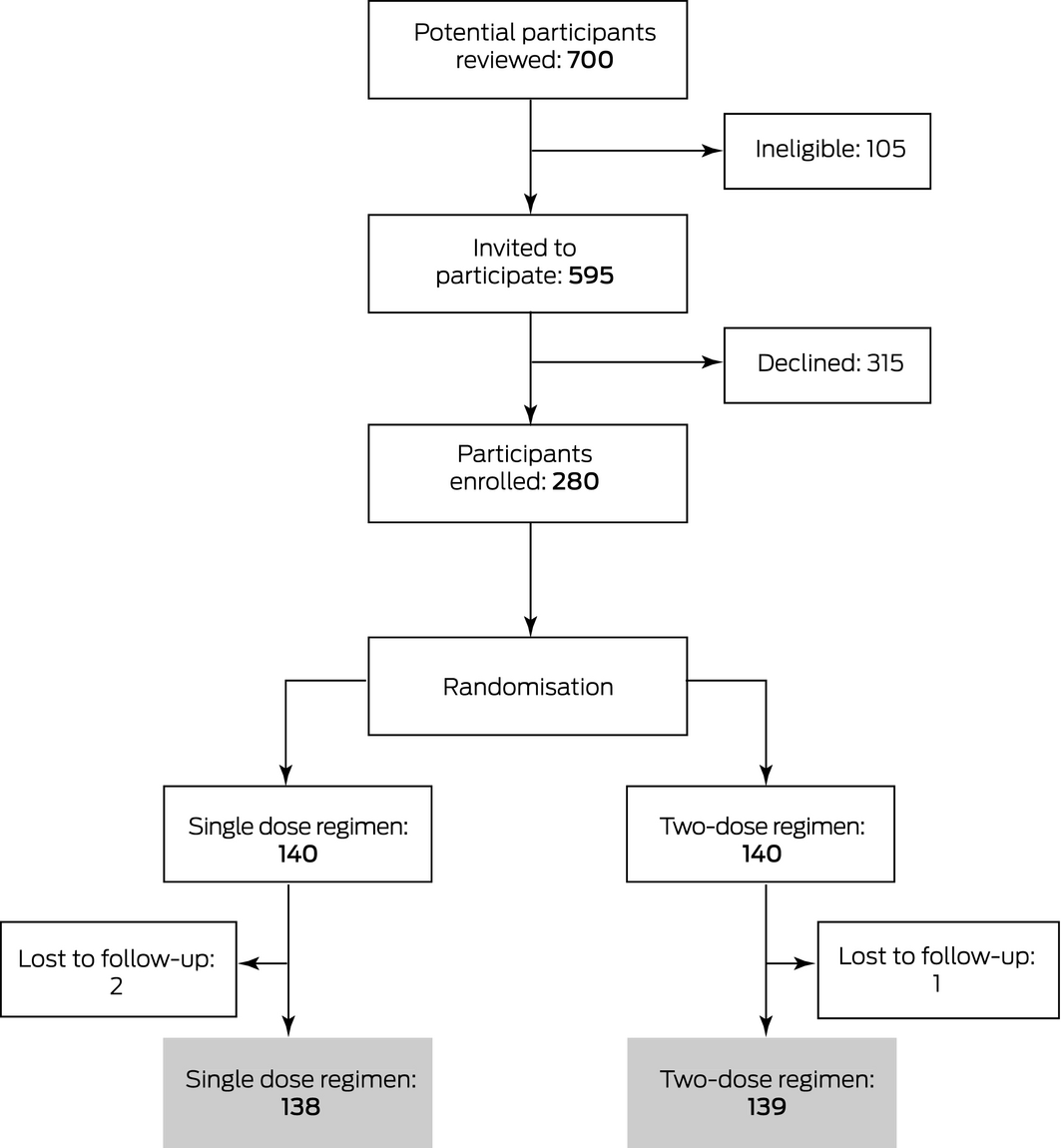



Single Dose V Two Dose Antenatal Anti D Prophylaxis A Randomised Controlled Trial The Medical Journal Of Australia



2




Rh Factor Sensitization Hap Diagram Quizlet




Sensitivity Of Fetal Rhd Screening For Safe Guidance Of Targeted Anti D Immunoglobulin Prophylaxis Prospective Cohort Study Of A Nationwide Programme In The Netherlands The Bmj




Rhophylac Solution For Injection Nps Medicinewise




Pdf Guideline For Blood Grouping And Red Cell Antibody Testing In Pregnancy




Anti D Prophylaxis For Rhesus D Rhd Negative Women Having An Abortion Of A Pregnancy Up To 13 6 Weeks Gestation A Systematic Review And New Nice Consensus Guidelines Bmj Sexual Reproductive Health




Management Of The Rhesus Negative Mother
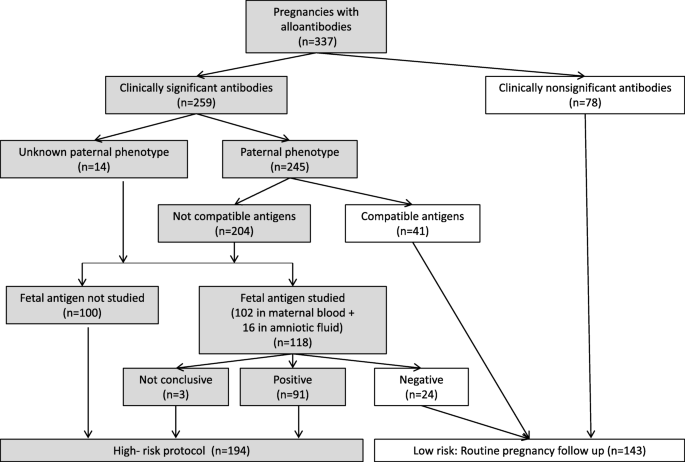



Management And Outcome Of Pregnancies In Women With Red Cell Isoimmunization A 15 Year Observational Study From A Tertiary Care University Hospital Bmc Pregnancy And Childbirth Full Text




Anti D Prophylaxis Dr Shashikala
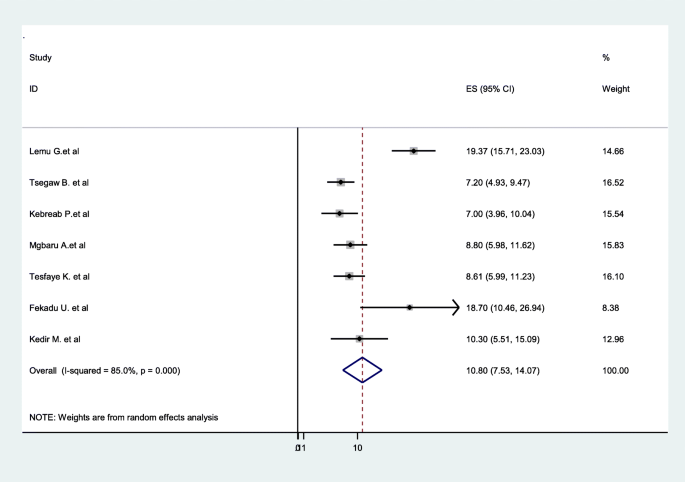



Prevalence Of Rhesus D Negative Blood Type And The Challenges Of Rhesus D Immunoprophylaxis Among Obstetric Population In Ethiopia A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Maternal Health Neonatology And Perinatology Full Text



Targeted Antenatal Anti D Prophylaxis For Rhd Negative Pregnant Women A Systematic Review Bmc Pregnancy And Childbirth Full Text




Variants Of Rhd Current Testing And Clinical Consequences Daniels 13 British Journal Of Haematology Wiley Online Library




Pdf Guideline For Blood Grouping And Red Cell Antibody Testing In Pregnancy




Platelet Transfusion Alloimmunization And Management Of Platelet Refractoriness Professional Education



Rh Negative Pregnancy And The Management Of Rh Immunized Pregnancy Flashcards Cram Com




Management Of Rhesus Negative Mother Pdf Free Download




Pdf Anti D Prophylaxis Reviewed In The Erea Of Foetal Rhd Genotyping




Diagnosis And Management Of Ectopic Pregnancy American Family Physician




Alloimmunization In Pregnancy Ppt Video Online Download



Rh Negative Mother Management Paras




Rhogam Redux Taming The Sru




Management Of Rhesus Negative Mother Pdf Free Download




Non Invasive Fetal Rhd Genotyping A Rapid Qualitative Review Ncbi Bookshelf




Management Algorithm For Pregnancies Complicated By Anti D Anti K Or Download Scientific Diagram




Being Rhesus D Negative In Pregnancy Queensland Maternity And




Approach To Red Blood Cell Antibody Testing During Pregnancy The College Of Family Physicians Of Canada



Fetal Hemolytic Disease Content Last Reviewed 15th February 18 Chapter 12 High Risk Pregnancy



2




Jaypeedigital Ebook Reader



Hemolytic Disease Of The Newborn Treatment Management Approach Considerations Medical Care Complications



Management Of The Rhesus Negative Mother




Management Of Rhesus Alloimmunization In Pregnancy Sciencedirect



2




Pdf Anti D Prophylaxis For Rhesus D Rhd Negative Women Having An Abortion Of A Pregnancy Up To 13 6 Weeks Gestation A Systematic Review And New Nice Consensus Guidelines



Thyroid Disorders In Pregnancy And Postpartum Australian Prescriber



2




Editor S Choice European Society For Vascular Surgery Esvs 21 Clinical Practice Guidelines On The Management Of Venous Thrombosis European Journal Of Vascular And Endovascular Surgery



Faq S Southern Blood Services Inc




Guideline For Blood Grouping And Red Cell Antibody Testing In Pregnancy White 16 Transfusion Medicine Wiley Online Library



2
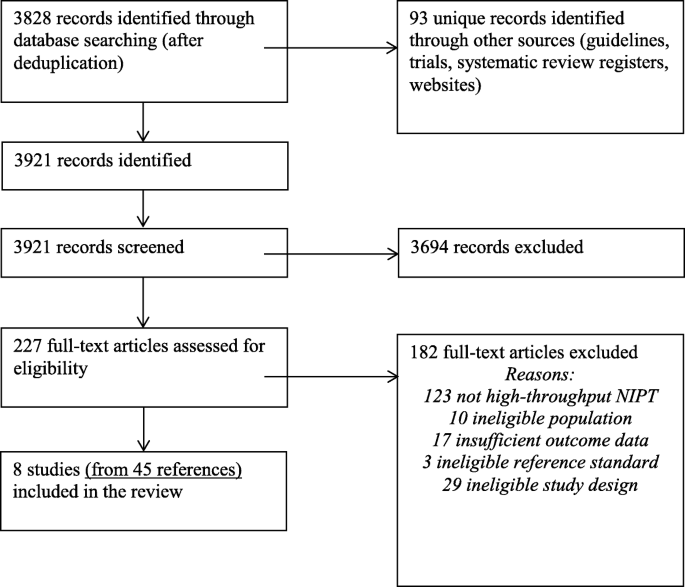



High Throughput Non Invasive Prenatal Testing For Fetal Rhesus D Status In Rhd Negative Women A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Bmc Medicine Full Text




First Trimester Bleeding Advances In Family Practice Nursing




Hemolytic Disease Of The Fetus And Newborn And Perinatal Immune Thrombocytopenia Professional Education




Rh Factor Definition Of Rh Factor By Medical Dictionary




No 348 Joint Sogc Ccmg Guideline Update On Prenatal Screening For Fetal Aneuploidy Fetal Anomalies And Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes Journal Of Obstetrics And Gynaecology Canada



2
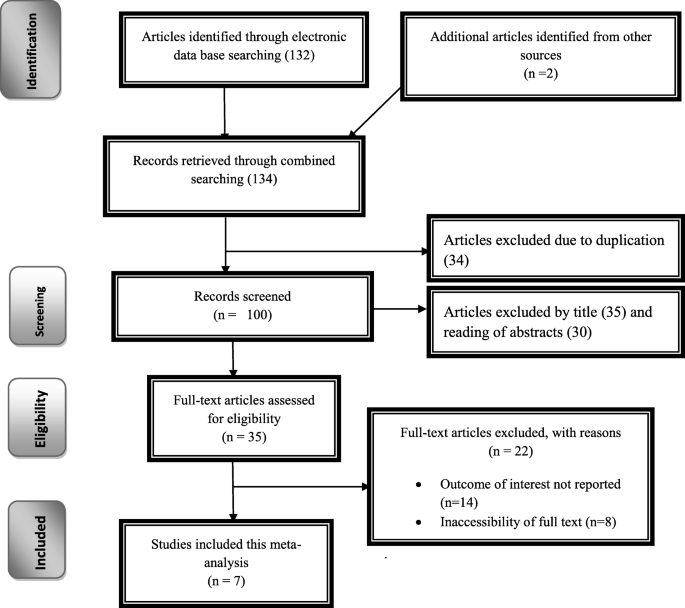



Prevalence Of Rhesus D Negative Blood Type And The Challenges Of Rhesus D Immunoprophylaxis Among Obstetric Population In Ethiopia A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Maternal Health Neonatology And Perinatology Full Text
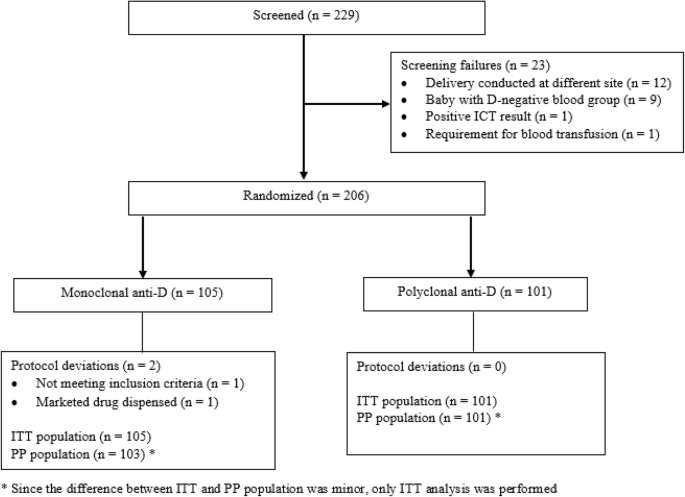



A Multicenter Randomized Open Label Trial Comparing The Efficacy And Safety Of Monoclonal Anti Rh D Immunoglobulin With Polyclonal Anti Rh D Immunoglobulin For The Prevention Of Maternal Rh Isoimmunization Springerlink



1




First Trimester Bleeding Evaluation And Management American Family Physician



Q Tbn And9gcqmrwe3mskoo Zz8vlr6md6r8c Qegpky1u0gyuaq7saypbbmo Usqp Cau



2
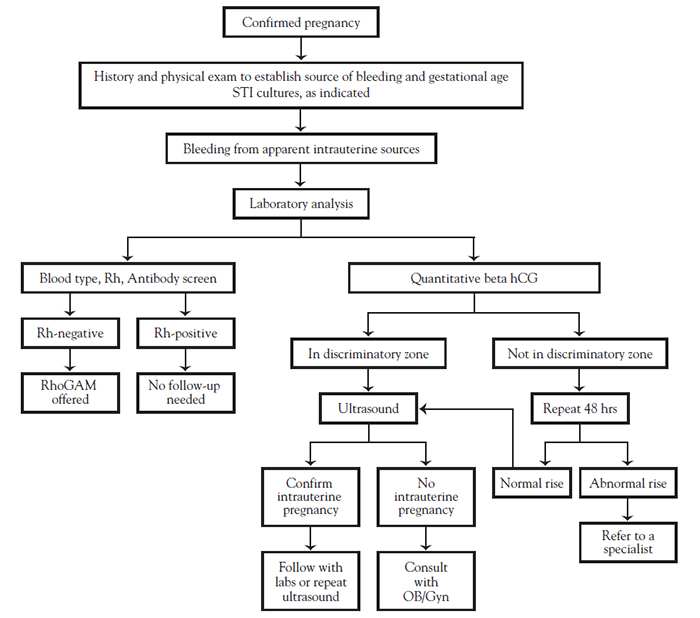



Course Content Bleeding During Pregnancy Netce




Rhesus Factor Hd Stock Images Shutterstock
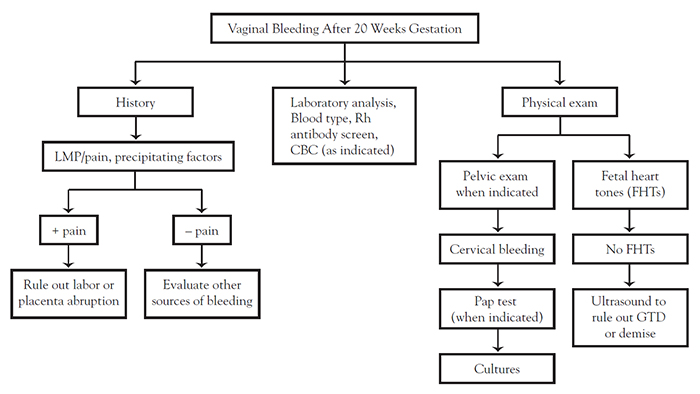



Course Content Bleeding During Pregnancy Netce




Management Of Rh Negative Pregnancy




Utility Of Anti D Immunoglobulin Rho Gam During First Trimester Pregnancy Core Em




Trauma In Pregnancy An Updated Systematic Review American Journal Of Obstetrics Gynecology




Treatment And Prevention Of Rh Isoimmunization Springerlink



2




File Doctorswriting




sh Guideline For The Use Of Anti D Immunoglobulin For The Prevention Of Haemolytic Disease Of The Fetus And Newborn Qureshi 14 Transfusion Medicine Wiley Online Library




Trauma In Pregnancy Assessment Management And Prevention American Family Physician




Society For Maternal Fetal Medicine Smfm Clinical Guideline 8 The Fetus At Risk For Anemia Diagnosis And Management American Journal Of Obstetrics Gynecology




sh Guideline For The Use Of Anti D Immunoglobulin For The Prevention Of Haemolytic Disease Of The Fetus And Newborn Qureshi 14 Transfusion Medicine Wiley Online Library



2
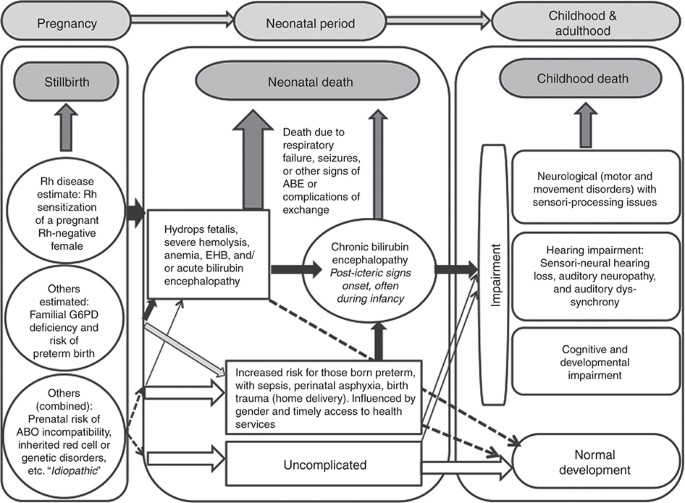



Neonatal Hyperbilirubinemia And Rhesus Disease Of The Newborn Incidence And Impairment Estimates For 10 At Regional And Global Levels Pediatric Research



Antenatal And Postpartum Prevention Of Rh Alloimmunization A Systematic Review And Grade Analysis




Hemolytic Disease Of The Fetus And Newborn And Perinatal Immune Thrombocytopenia Professional Education




Rhogam Redux Taming The Sru



Oman Medical Journal Archive




Anti D Ig Prophylaxis Guidelines Fogsi Hematology Immunology
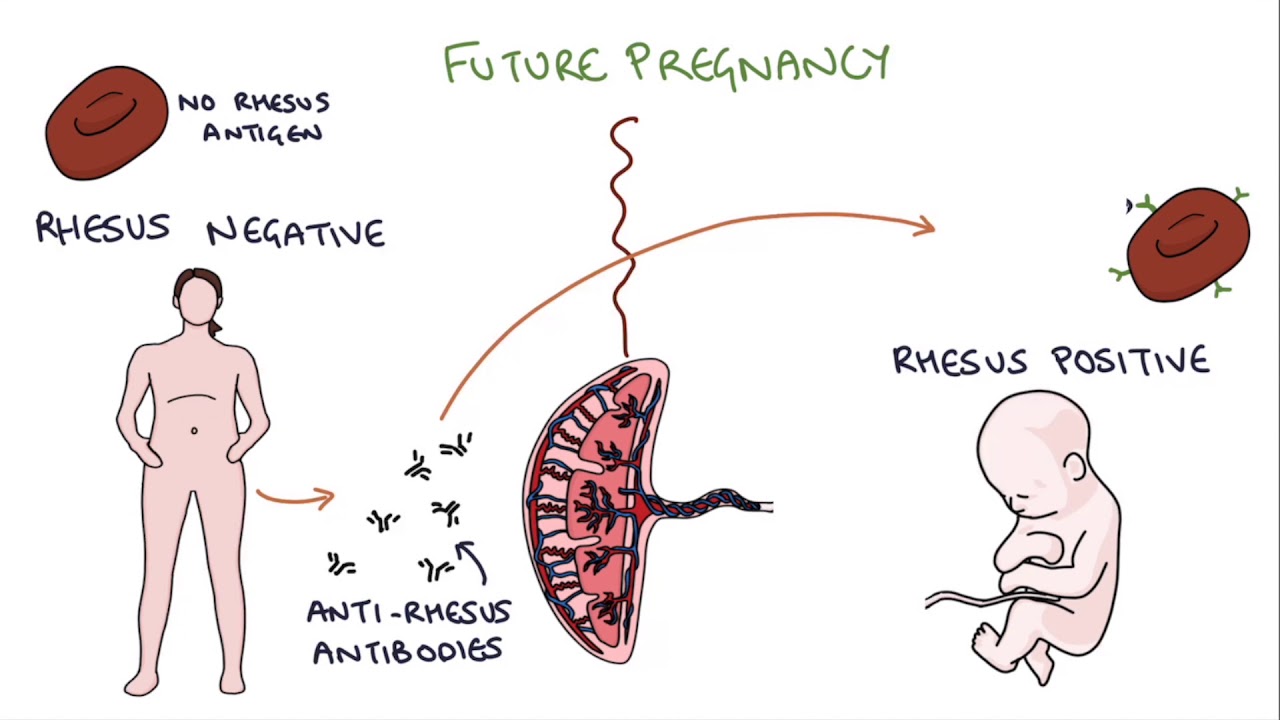



Understanding Rhesus Status And Anti D In Pregnancy Youtube



Targeted Antenatal Anti D Prophylaxis For Rhd Negative Pregnant Women A Systematic Review Bmc Pregnancy And Childbirth Full Text




First Trimester Bleeding Evaluation And Management American Family Physician




Guideline For Blood Grouping And Red Cell Antibody Testing In Pregnancy White 16 Transfusion Medicine Wiley Online Library



1




Anti D Preventing Rhesus Isoimmunisation Nurse Key


コメント
コメントを投稿